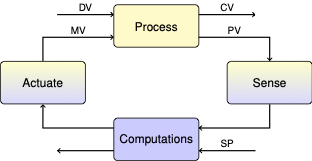
Lab 3: Relay (On-Off) Control#
Your Name:
In this lab assignment you will implement relay control for the Temperature Control Laboratory. The class website explains the Python interface to the TCLab in more detail. Your main tasks are:
Use numerical simulation to tune your controller (Exercise 0)
Implement and test a relay control for the heater/sensor system
Implement and test a relay control to track a complex setpoint (dark chocolate tempering)
Our labratory assignments this semester build up each other. For best results, you want to use the same hardware configuration for each lab. To help with this, please fill in the following:
TCLab: Did you use your own TCLab or borrow one (friend, class set)?
Power adapter: How did you plug the TCLab into power? Did you use the adapter that came with your kit, a different USB power adapter, or one of the plugs in our computer classroom? What is the power rating of the adapter? (e.g., 1A or 2A or 2.1A at 5V?, Was the power adapter/USB port labeled “phone” or “tablet”?)
Suggestion: take a picture of your TCLab setup including the power adapter. Keep this on your phone until the end of the semester.
Exercise 0. Simulation#
This exercise is due BEFORE the start of lab. It is a pre-lab assignment. Your task:
Read the entire lab assigment. If you have a question, post to Canvas.
Create a plot showing the setpoints described in Excercise 1.
On paper (or a tablet), write down the system of differential equations for the TCLab with the simple relay controller described in Exercise 1. Include in your model the intial conditions for each state.
Formulate your differential equations as a linear time invariant (LTI) system in cannonical state-space form (use matrices \(\mathbf{A}\), \(\mathbf{B}\), \(\mathbf{C}\), and \(\mathbf{D}\)) with a few extra equations for the control law. Write this out on paper.
Hint: You can assume your two TCLab channels are identical and there is no interaction between the channels. It will be an imperfect model, but you have enough information to build it. Here are some ideas from a legacy page on the class website.
Using Python, numerically simulate the system of differential equations. Look at this example. Use the TCLab model parameters you estimated in Lab 2 for your personal TCLab hardware.
Visualize Setpoints#
### Create a plot showing the setpoints described in Exercise 1
# Set default parameters for publication quality plots
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
SMALL_SIZE = 14
MEDIUM_SIZE = 16
BIGGER_SIZE = 18
plt.rc('font', size=SMALL_SIZE) # controls default text sizes
plt.rc('axes', titlesize=SMALL_SIZE) # fontsize of the axes title
plt.rc('axes', labelsize=MEDIUM_SIZE) # fontsize of the x and y labels
plt.rc('xtick', labelsize=SMALL_SIZE) # fontsize of the tick labels
plt.rc('ytick', labelsize=SMALL_SIZE) # fontsize of the tick labels
plt.rc('legend', fontsize=SMALL_SIZE) # legend fontsize
plt.rc('figure', titlesize=BIGGER_SIZE) # fontsize of the figure title
plt.rc('lines', linewidth=3)
# modify these setpoints to change with time
def SP1_simple(t):
"""Set point definition for T1
Arguments:
t: time (s)
Returns:
set point of T1
"""
return 35
def SP2_simple(t):
"""Set point definition for T2
Arguments:
t: time (s)
Returns:
set point of T2
"""
return 40
# Add your solution here
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Add your solution here
Function to Numerically Simulate Relay Controller#
### Simulate differential equations for the TCLab system plus relay controller
def tclab_simulate_relay(SP1, SP2, param,
d=0.1, dt=1, T_amb=24, tend=500,
alpha=0.00016, P1=200, P2=200,
verbose=False, plot=True):
''' Simulate the TCLab system with relay control
Arguments:
SP1: function that returns setpoint for T1
SP2: function that returns setpoint for T2
param: list of parameters [Ua, Ub, Uc, CpH, CpS]
d: deadband in temperature control, default is 0.5 C
dt: time step, default is 1 second
T_amb: ambient temperature, default is 24 C
tend: end time for simulation, default is 500 seconds
alpha: heat transfer coefficient, default is 0.00016
P1: power level for heater 1, default is 200
P2: power level for heater 2, default is 200
verbose: print matrices, default is False
plot: create plots, default is True
Returns:
data: DataFrame with columns for Time, T1, T2, Q1, Q2
'''
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Parameters
Ua, Ub, Uc, CpH, CpS = param
# Hint: You need to define the system matrices A, B, C, and D
# Assume the state vector is x = [T1H, T1S, T2H, T2S]
# Assume the input vector is u = [Q1, Q2]
# Add your solution here
if verbose:
# Print the matrices
print("Matrix A:\n", A)
print("\nMatrix B:\n", B)
print("\nMatrix C:\n", C)
print("\nMatrix D:\n", D)
# Convert A and B matrices to discrete time using zero-order hold
# Zero-order hold: assumes input is constant during time interval
# This is a reasonable assumption for our system
from scipy.signal import cont2discrete
d_system = cont2discrete((A, B, C, D), dt, method='zoh')
# Extract the discrete time A and B matrices
Ad = d_system[0]
Bd = d_system[1]
Cd = d_system[2]
Dd = d_system[3]
if verbose:
print("\nDiscrete-time A matrix:\n", Ad)
print("\nDiscrete-time B matrix:\n", Bd)
print("\nDiscrete-time C matrix:\n", Cd)
print("\nDiscrete-time D matrix:\n", Dd)
# Define time
t = np.arange(0, tend, dt)
n = len(t)
# Initialize state matrix
X = np.zeros((n, 4))
# Initialize input matrix
U = np.zeros((n, 2))
# Initialize setpoints
SP = np.zeros((n, 2))
# Loop over time steps
for i in range(n):
# Current state
x = X[i, :]
# Unpack into individual states
T1H, T1S, T2H, T2S = x
# Setpoints
sp1 = SP1(t[i])
sp2 = SP2(t[i])
# Temperature control
# Channel 1
# Hint: Write code below to set U[i,0]
# Look at the equations you wrote down for the relay controller
# Add your solution here
# Channel 2
# Hint: Write code below to set U[i,1]
# Add your solution here
# Update state
if i < n-1:
# Do not update the state for the last time step
# We want to update U and SP for plotting
X[i + 1, :] = Ad @ x + Bd @ U[i, :]
# Save step points
SP[i, 0] = sp1
SP[i, 1] = sp2
# Shift states from deviation variables to absolute values
X += T_amb
# Create DataFrame
data = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=['T1H', 'T1S', 'T2H', 'T2S'])
data['Time'] = t
data['Q1'] = U[:, 0]
data['Q2'] = U[:, 1]
data['SP1'] = SP[:, 0]
data['SP2'] = SP[:, 1]
if plot:
plt.title('Channel 1, Simulated Relay Control with d={} (C)'.format(d))
plt.step(data['Time'], data['T1H'], label='T1H', linestyle='--')
plt.step(data['Time'], data['T1S'], label='T1S', linestyle='-')
plt.step(data['Time'], data['SP1'], label='SP1', linestyle='-.', color='black', alpha=0.5)
plt.ylabel('Temperature (C)')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Add code to plot Channel 2
# Add your solution here
plt.title('Heaters, Simulated Relay Control with d={} (C)'.format(d))
plt.step(data['Time'], data['Q1'], label='Q1')
plt.step(data['Time'], data['Q2'], label='Q2')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Power Level (%)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
return data
Simulate Controller with a Small Deadband Assuming No Cross Channel Interaction#
In Labs 1 and 2, we did not consider the second channel, so we do not have a good guess for the heat transfer rate between channels 1 and 2. To get started, lets assume there is NO heat transfer between channels, i.e., \(U_c = 0\).
# Ua, Ub, Uc, CpH, CpS
# Update these to match the parameters of your system (from Lab 2)
tclab_parameters_no_interaction = [0.050, 0.099, 0, 7.399, 1.663]
sim1 = tclab_simulate_relay(SP1_simple, SP2_simple, tclab_parameters_no_interaction, d=0.2)
Simulate Controller with a Small Deadband Assuming Small Cross Channel Interaction#
Next, let’s repeat the simulation, but assume the heat transfer between channels is 50% the rate of each channel with the ambient, i.e., \(U_c = 0.5 U_a\)
tclab_parameters_with_interaction = tclab_parameters_no_interaction.copy()
tclab_parameters_with_interaction[2] = tclab_parameters_with_interaction[0]*0.5
sim2 = tclab_simulate_relay(SP1_simple, SP2_simple, tclab_parameters_with_interaction, d=0.2)
Simulate the Controller with a Large Deadband and No Cross Channel Interaction#
Now, let’s consider a larger deadband with \(U_c = 0\).
sim3 = tclab_simulate_relay(SP1_simple, SP2_simple, tclab_parameters_no_interaction, d=2)
Simulate the Controller with a Large Deadband and Modest Cross Channel Interaction#
Finally, consider a larger deadband and \(U_c = 0.5 U_a\).
sim4 = tclab_simulate_relay(SP1_simple, SP2_simple, tclab_parameters_with_interaction, d=2)
# Optional extra code cell
# Please delete this cell if you do not use it
# Add your solution here
Discussion#
Write a few observations about your simulation results. (Recommendation: Write 3 to 5 bullet points where each bullet point is one idea, expressed in one or two sentences.)
Answer:
Exercise 1. Simple Relay Control for TC Lab#
Create a relay controller subject to the following requirements:
Simultaneous control of sensor temperatures \(T_1\) and \(T_2\) to setpoints 35 and 40 °C, respectively. The setpoints return to 25 °C at t = 300.
Use a tolerance value \(d\) of 0.5 °C.
Set the minimum and maximum values of the heater to 0 and 100%, respectively.
Set ‘lab.P1’ and ‘lab.P2’ to 200 to be consistent with prior labs.
Run the experiment for at least 500 seconds.
Show the results of an experiment in which the setpoints are adjusted accordingly.
Debug Your Implementation with the TCLab Digital Twin#
The tclab library includes a simulation-mode/digital twin. This allows you to debug your controller code BEFORE using your hardware. This is really helpful as the digital twin does not require anytime to cool down.
Here is the code to use the digital twin:
TCLab = setup(connected=False, speedup=5)
Setting connected=False enables the simulation-mode (a.k.a., digital twin). When connected=False, you can also use the speedup argument to speed-up the simulation. Again, this is super helpful for debugging your code.
With great power comes great responsibility. While the digital twin mode is increadibly helpful, it is very easy to forget to set connected=True again before running the actual experiments in the lab. In later Exercises, you must run the experiments on your TCLab hardware. It is important you tripple check connected=True.
Below is some starter code.
# As a first step, let's verify the sample code runs
# After that, modify the code to implement the relay controller for T2
# Debug your implementation with the connected=False
# "digital twin" mode before connecting to the real device
from tclab import TCLab, clock, Historian, Plotter, setup
''' Important note about the 'setup' function:
connected=False is used for the simulation.
connected=True is used to connect to the real device.
speedup=5 can be used to run the simulation at 5x real time.
'''
TCLab = setup(connected=False, speedup=5)
# relay controller
def relay(SP, d=0.5, Umin=0, Umax=100):
"""Relay controller definition
Arguments:
SP: set point function
d: set point tolerance
Umin: minimum heater output (%)
Umax: maximum heater output (%)
Returns:
none
"""
#start with the heater off
U = 0
#while the simulation is active (t<tfinal)
while True:
t, T = yield U
#When T is below the set point, turn on heater
if T < SP(t) - d:
U = Umax
#When T is above the set point, turn off heater
if T > SP(t) + d:
U = Umin
# create a single control loop for T1
controller1 = relay(SP1_simple)
controller1.send(None)
# This started code only implements a controller for T1
# What do you need to change to implement a controller for T2 too?
# simulate with TCLab
t_final = 60 # change this to 500 seconds for the actual experiment
t_step = 1
with TCLab() as lab:
sources = [("T1", lambda: lab.T1), ("T2", lambda: lab.T2),
("SP1", lambda: SP1_simple(t)), ("SP2", lambda: SP2_simple(t)),
("Q1", lab.Q1), ("Q2", lab.Q2)]
#load historian
h = Historian(sources)
#load plotter
p = Plotter(h, t_final, layout=(("T1", "SP1"), ("T2", "SP2"), ("Q1", "Q2")))
#While time is less than tfinal
for t in clock(t_final, t_step):
## Controller for T1
# This starter code only manipulates U1 to control T1.
# Your specifications also give a setpoint for T2
T1 = lab.T1
# Send the controller time and T1 data
U1 = controller1.send([t, T1])
lab.Q1(U1)
## Controller for T2
# What do you need to change to implement a controller for T2 too?
## Read data and update plot
p.update()
Verify your Device is at Ambient Temperature#
# Verify your device has cooled back to ambient
tfinal = 30 #seconds
run_tclab = True
"""
In the labs, we will us "run_tclab" to control whether the TCLab is used.
After you finish the lab experiment, set run_tclab = False.
This way, you can run all the cells without losing your TCLab output.
"""
if run_tclab:
# Connect to the TCLab device (not digital twin)
# This should be connected=True
TCLab = setup(connected=True)
# perform experiment
with TCLab() as lab:
#Set power to 0
lab.U1 = 0
lab.U2 = 0
#load historian
h = Historian(lab.sources)
#Load plotter
p = Plotter(h, tfinal)
#While time is less than tfinal
for t in clock(tfinal):
#Read data and update plot
p.update(t)
Perform the Experiment with TCLab Hardware#
Hint: You already debugged the code above with connected=False. You should copy your code to below and slightly modify. A few hints:
You should not copy functions you already defined.
Be careful with the indentation. You may get an error about the device not being connected. If that occurs, check the indentation.
Make sure you adjust
t_final
# Copy the code you implemented and debugged above
import os.path
data_file_simple = 'lab3-simple-relay.csv'
def save_data(history, data_file, overwrite_file=False):
''' Save the data to a csv file
Arguments:
history: dataframe with data
data_file: filename to save data
overwrite_file: boolean to overwrite file, default is False to prevent accidental overwriting
'''
if not overwrite_file and os.path.isfile('./'+data_file):
raise FileExistsError(data_file + ' already exisits. Either choose a new filename or set overwrite_file = True.')
else:
history.to_csv(data_file)
print("Successfully saved data to "+data_file)
if run_tclab:
# Connect to the TCLab device (not digital twin)
# This should be connected=True
TCLab = setup(connected=True)
# In the above cells, you debugged your logic for the relay controller with
# connected=False. Now, you can run the experiment with connected=True.
# Copy your code from above to below and run the experiment.
# Before you run this cell, make sure you have
# implemented the controller for T2
# This is the most common mistake in the lab.
# Indentation is the second most common mistake.
# The third most common mistake is rerunning with experiment
# without waiting for the device to cool back down to ambient.
# Add your solution here
save_data(h, data_file_simple, overwrite_file=False)
Discussion#
Write a 1 to 3 sentences to answer each of the following questions.
Q1 Describe the shape of the temperature profiles (time-series) for the exercise 1 experiment. Are these shapes expected?
Answer:
Q2 Speculate about why T1 overshoots the setpoint more than T2 in the exercise 1 experiment.
Answer:
Exercise 2. Tempering Chocolate#
We now want to create a relay controller that matches the temperature profile for tempering chocolate.
Temperature 1 specifications:
Start from ambient.
Reach 50 °C at 3 minutes, 27 °C at 7 minutes, return to 32 °C at 8 minutes, and hold until 10 minutes.
The goal is follow the linear ramp between setpoints as closely as possible.
Temperature 2 specifications:
Start from ambient, ramp, and then hold at 30 °C.
Hints:
Modify SP1 to linearly interpolate the set point as a function of time.
Plot the Described Temperature Profile#
# Complete these function to define the setpoints for T1 and T2
def SP1_chocolate(t):
"""Set point definition for T1
Arguments:
t: time (s)
Returns:
set point of T1
"""
# Add your solution here
def SP2_chocolate(t):
"""Set point definition for T2
Arguments:
t: time (s)
Returns:
set point of T2
"""
# Add your solution here
# Make a plot of the setpoints to verify your setpoint functions
# are correct.
# Add your solution here
Simulate the Chocolate Tempering Experiment#
One great way to test your setpoint functions is to simulate the response of the relay controller.
sim5 = tclab_simulate_relay(SP1_chocolate, SP2_chocolate, tclab_parameters_with_interaction, d=0.2)
Using this simulation, adjust \(d\) via trial-and-error. Choose a value of \(d\) and write a sentence or two to justify your choice. We care less about the value of \(d\) you select and more on your justification for the choice. This is an open ended question with many reasonable answers.
Answer:
Verify TCLab is at Ambient Temperature#
if run_tclab:
# Connect to the TCLab device (not digital twin)
# This should be connected=True
TCLab = setup(connected=True)
# Add your solution here
Perform the Experiment with TCLab Hardware#
Please use the value for \(d\) you identified above using the simulation.
# Copy your code from above and modify to match the specifications
data_file_chocolate = 'lab3-chocolate-relay.csv'
if run_tclab:
# You may optionally set connected=False to debug your code
# If you do, you MUST set it back to connected=True before running the experiment
# You should also rerun the code block above to verify your TCLab is at ambient temperature
# BEFORE running this experiment
TCLab = setup(connected=True)
# One of the most common mistakes is NOT using the correct
# setpoint functions when you copy and paste code from above.
# Add your solution here
save_data(h, data_file_chocolate, overwrite_file=True)
Discussion#
In the cholcate tempering simulation, how many times does each heater transitions from (a) one to off and (b) off to on? Fill in the table below.
Sensor |
On to Off |
Off to On |
|---|---|---|
T1 |
||
T2 |
Answer:
Descibe the shape of the T1 and T2 timeseries for the excerise 2 experiment. How do the T1 and T2 profiles relate to the on/off and off/on transitions for Q1 and Q2?
Answer:
Exercise 3. Quantify Tracking Error#
In this exercise, you will compare compute the error between the desired setpoint and the temperature sensor. We will use two metrics: root mean squared error (RMSE) and absolute mean error (AME):
Here \(N\) is the number of data points.
Create a Function to Quantify Controller Performance#
We will start by writing a general function that computer both tracking error metrics used save data and the setpoint function(s).
def compute_tracking_error(data, SP1, SP2=None):
''' Compute the tracking error between the set point and the data
Arguments:
data: dataframe with columns for T1 and T2
SP1: function that returns setpoint for T1
SP2: function that returns setpoint for T2, default None
Returns:
rmse1: root mean square error for T1
rmse2: root mean square error for T2
ame1: absolute mean error for T1
ame2: absolute mean error for T2
'''
# Grab the time data
if 'Time' in data.columns:
# if 'Time' is one of the columns
t = data['Time'].to_numpy()
else:
# otherwise, use the index
t = data.index.to_numpy()
if 'T1' in data.columns:
# for TCLab data, 'T1' is the column name
T1_name = 'T1'
elif 'T1S' in data.columns:
# for our simulation, 'T1S' is the column name
T1_name = 'T1S'
else:
raise ValueError('T1 data not found. Here are the column names: ' + str(data.columns))
if 'T2' in data.columns:
# for TCLab data, 'T2' is the column name
T2_name = 'T2'
elif 'T2S' in data.columns:
# for our simulation, 'T2S' is the column name
T2_name = 'T2S'
else:
T2_name = None
# Add your solution here
print('RMSE T1:\t',round(rmse1,2), 'C')
print('AME T1: \t',round(ame1,2), 'C')
if rmse2 is not None:
print('RMSE T2:\t',round(rmse2,2), 'C')
if ame2 is not None:
print('AME T2: \t',round(ame2,2), 'C')
return rmse1, rmse2, ame1, ame2
Performance of TCLab Device for Simple Experiment#
Next, use your function to analyze the simple experiment.
# Add your solution here
Performance of the Simulated Controller for the Simple Experiment#
Choose one of the simulation results from Exercise 0 and compute the performance.
# Add your solution here
Performance of TCLab Device for Chocolate Experiment#
Next, analyze the chocolate tempering experiment.
# Add your solution here
Performance of the Simulated Controller for the Chocolate Experiment#
Finally, analyze the simulation for the chocolate experiment.
# Add your solution here
Summary#
Complete the following table to summarize your results.
Experiment |
Mode |
RMSE T1 |
AME T1 |
RMSE T2 |
AME T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Simple |
Hardware |
||||
Simple |
Simulate |
||||
Chocolate |
Hardware |
||||
Chocolate |
Simulate |
Concluding Discussion#
The following questions tie together the Exercises throughout the lab. Please write 1 to 3 sentences per prompt.
Q1 How can we reduce the oscillations in these experiments? Propose at least one idea and provide reasoning for why it could work.
Answer:
Consider the following feedback diagram from the first day of class:
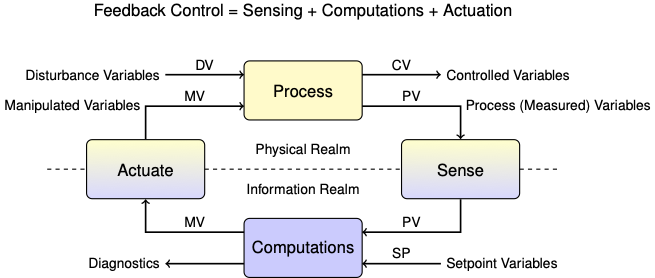
Identify the variables in each of the categories for our temperature control lab.
Maninpulated Variable(s):
Answer:
Controlled Variable(s):
Answer:
Process/Measured Variable(s):
Answer:
Set Point Variable(s):
Answer:
Disturbance Variable(s):
Answer:
Bonus Exercise (Extra Credit)#
Using your code from Lab 2 as a starting point, re-estimate the parameters in the four-state TCLab model (\(T_S\) and \(T_H\) for both channels). Perform simultaneous nonlinear regression with four datasets:
Step test (Lab 1)
Sine test (Lab 2)
Simple Relay On/Off Experiment (Lab 3)
Chocolate Tempering Relay On/Off Experiment (Lab 3)
You should start by deriving the four state model on paper. You may need to perform multi-start initialization. Include time-series plots, analysis of the residuals, and quantification of uncertainty, similar to Lab 2. How much did your parameter estimates change compared to Lab 2? How much did the parameter uncertainty decrease (or increase)? Do the results make sense and why?
# Add your solution here
return [dT1H, dT1S, dT2H, dT2S]
soln = solve_ivp(deriv, [min(t_expt), max(t_expt)], [T_amb, T_amb], t_eval=t_expt)
T1H = soln.y[0]
T1S = soln.y[1]
T2H = soln.y[2]
T2S = soln.y[3]
if plot:
# Plot the temperature data and heat power
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.plot(t_expt, data['T1'], 'ro', label='Measured $T_S$')
plt.plot(t_expt, T1S, 'b-', label='Predicted $T_{S1}$')
plt.plot(t_expt, T1H, 'g-', label='Predicted $T_{H1}$')
plt.plot(t_expt, T2S, 'r-', label='Predicted $T_{S2}$')
plt.plot(t_expt, T2H, 'p-', label='Predicted $T_{H2}$')
plt.ylabel('Temperature (degC)')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.plot(t_expt, data['Q1'], 'g-', label='Heater 1')
plt.plot(t_expt, data['Q2'], 'p-', label='Heater 2')
plt.ylabel('Heater (%)')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Time (sec)')
plt.title(plot_title)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return TS
# Test your function with the data and initial parameters
TS = tclab_model4(data, [0.1, 0.2, 4, 0.1], plot=True)
### END SOLUTION
Common Mistakes#
Not using the correct kernel (for the controls environment with TCLab installed)
Not setting up controller #2 (This includes assigning T2 and Q2 in the simulation code)
When switching to
connected=Truemost got errors if they did not restart the kernel and clear all the cells outputTrying to create their own linear interpolation function, just use
np.interp
Declarations#
TCLab Hardware: Did you use the same TCLab device for Labs 1, 2, and 3? If not, please provide details here. These labs are designed to use the same hardware throughout the semester. Please keep this in mind as you answer the discussion questions, especially when comparing the simulated to actual performance.
Collaboration: If you worked with any classmates, please give their names here. Describe the nature of the collaboration.
Generative AI: If you used any Generative AI tools, please elaborate here.
Reminder: The written discussions responses must be in your own words. Many of these questions ask about your specific results or are open-ended questions with many reasonable answers. Thus we expect unique responses, analyses, and ideas.
We may use writing analysis software to check for overly similar written responses. You are responsible for reviewing the colaboration policy outlined in the class syllabus to avoid violations of the honor code.