1.2. Elements of Process Control#
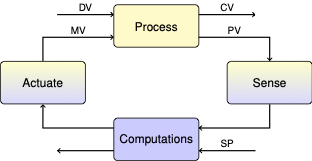
1.2.1. Feedback Control#
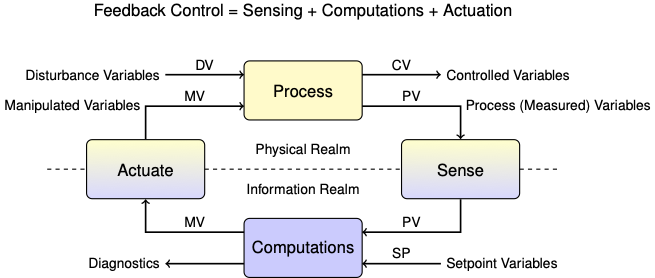
1.2.2. System Variables#
DV: Disturbance Variables: External variables that impose changes on the system under study.
MV: Manipulated Variables: Variables that can be manipulated in order to acheive a desired response.
CV: Controlled Variables: System variables that are the targets of the control actions.
PV: Process Variables: System variables that are measured for the purpose of control. Ideally these would be the same as the controlled variables. Frequently, however, values of the controlled variable must be inferred from variables that can be measured with the available instrumentation.
SP: Setpoint Variables: Desired values for the controlled variables.
Diagnostics: Control system outputs indicating the internal state or condition of the process or controller.
1.2.3. Controllers#

1.2.4. Sensors#
There are only two methods to determine if a process is operating properly. The most direct method is to directly measure the variables of interest. If you’re trying to control the temperature of a process stream, then a direct measurement of temperature is likely the most effective
1.2.4.1. The “Big Four”#
Thermocouples

Platinum resistance
Thermisters
Infrared Imaging sensors
Pressure

Level
Flow
1.2.4.2. A “Cast of Thousands”#
Position
Composition
Humidity
Accelerators
Magnetic field
1.2.5. Actuators#
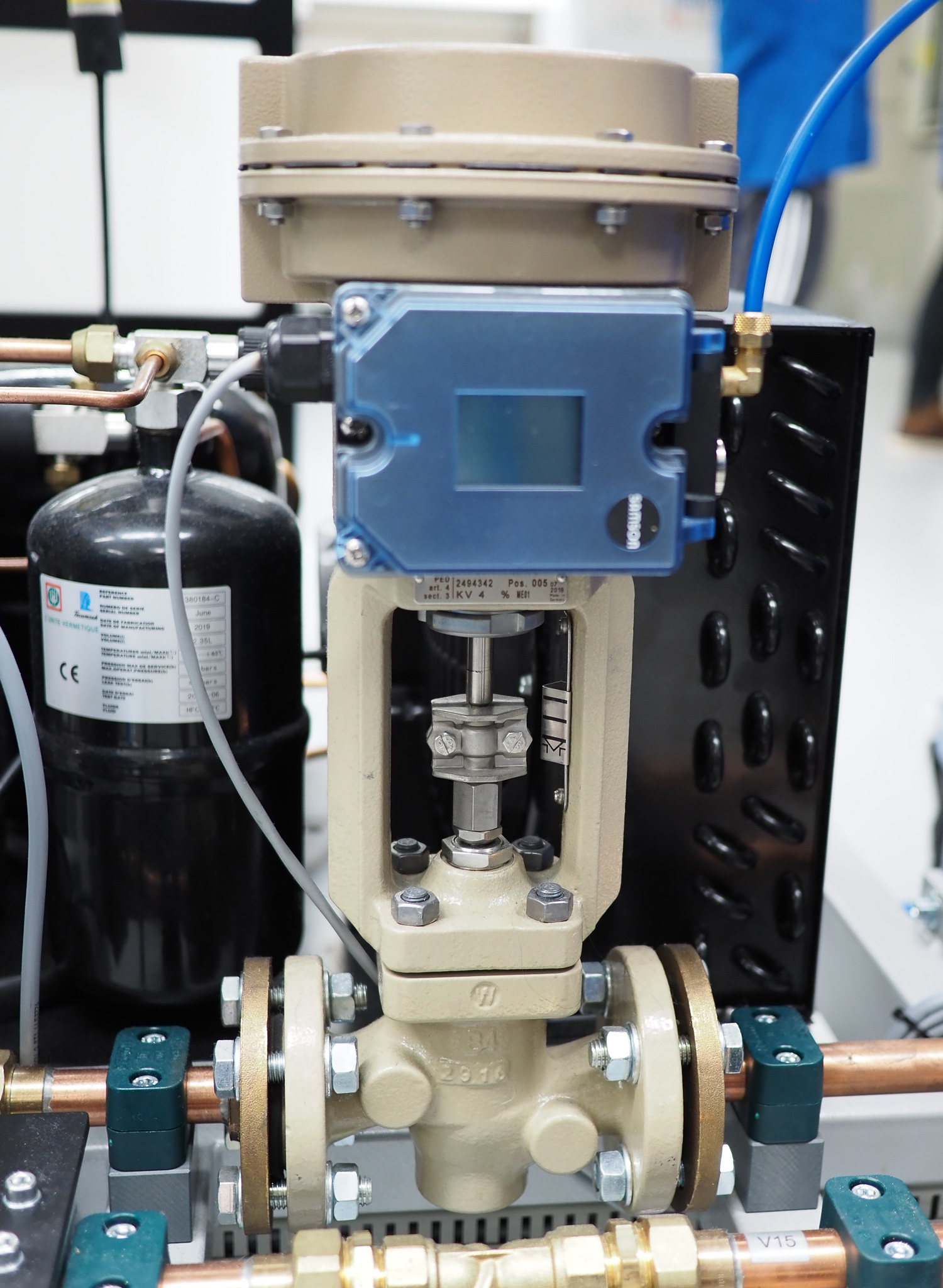
1.2.5.1. Control Valves#
Solenoid Valves (On/Off)

Proportional Control Valves

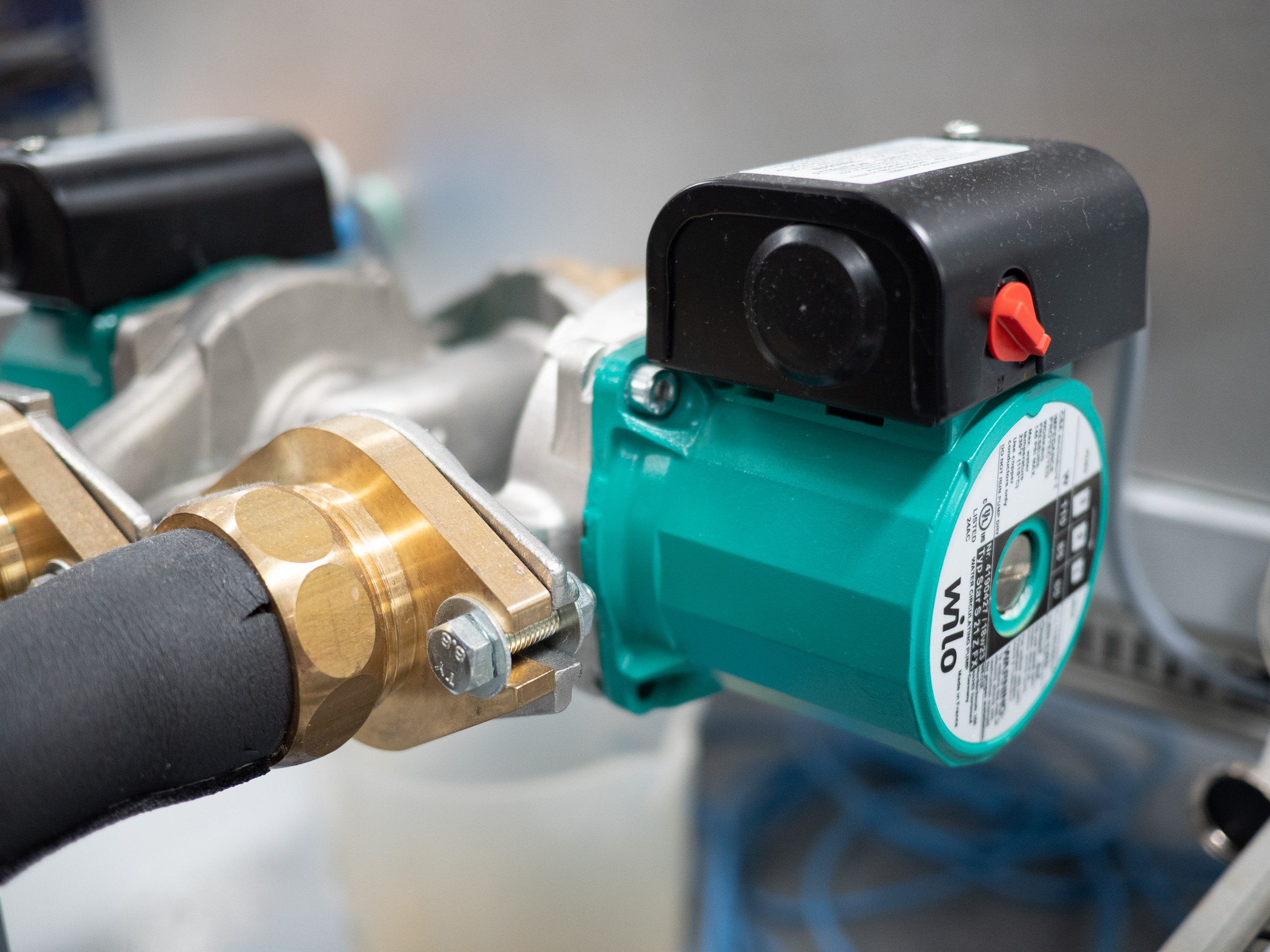
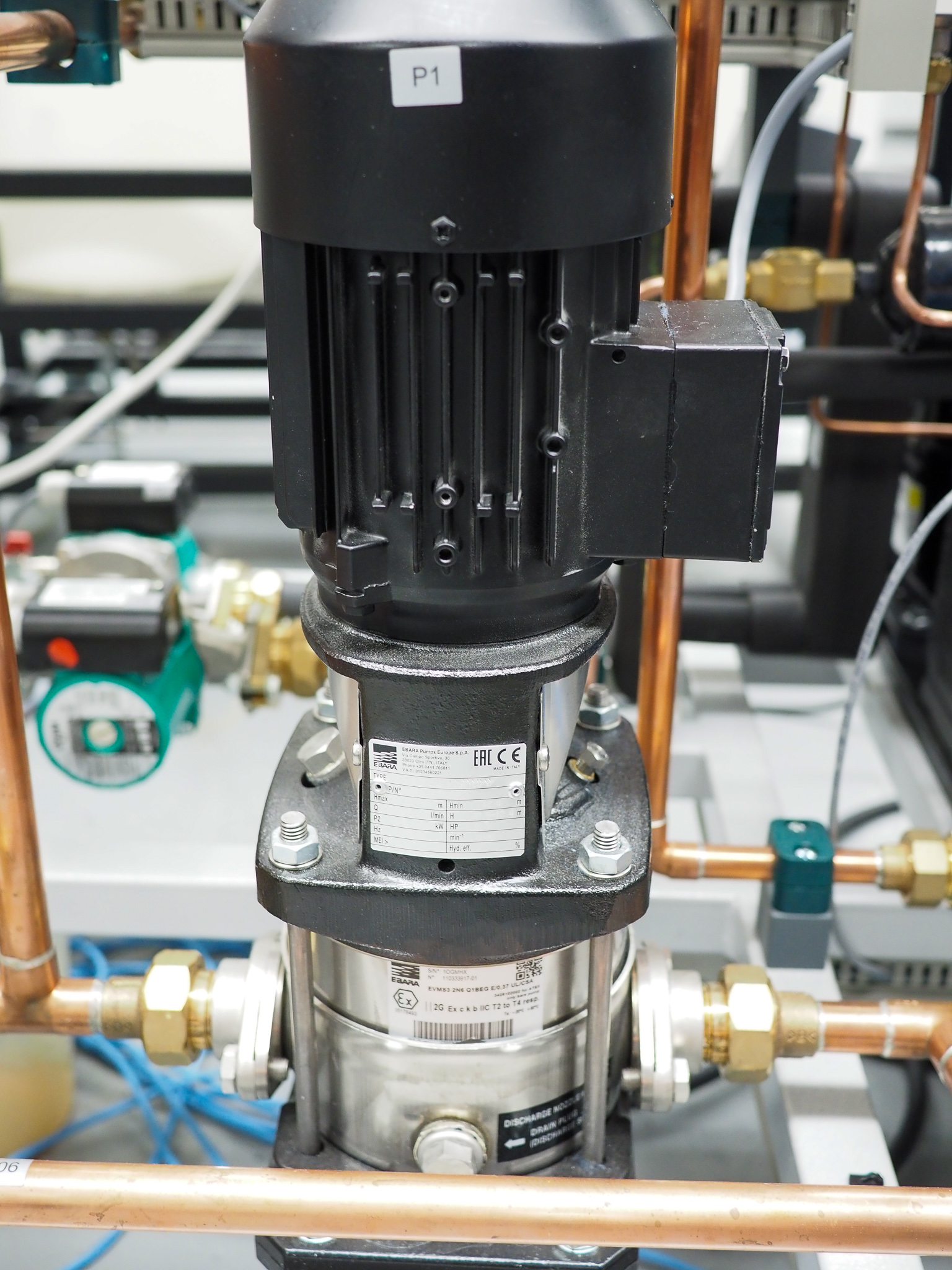
1.2.5.2. Pumps#


Heaters
Positioners/Motors/Servos