Reference Section 4.2 in Biegler (2010)
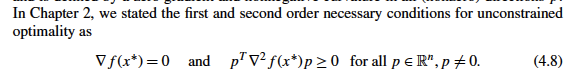

Consider the following two dimensional optimization problem:
$$ \begin{align} \min_{x_1,x_2} \quad & f(x) := x_1^2 - 4 x_1 + \frac{3}{2} x_2^2 -7x_2 + x_1 x_2 + 9 - \mathrm{ln}(x_1) - \mathrm{ln}(x_2) \\ \mathrm{s.t.} \quad & g(x) := 4 - x_1 x_2 \leq 0 \\ & h(x) := 2 x_1 - x_2 = 0 \end{align} $$import numpy as np
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyomo.environ import *
## Objective function
def f(x):
return x[0]**2 - 4*x[0] + 1.5*x[1]**2 - 7*x[1] + x[0]*x[1] + 9 - np.log(x[0]) - np.log(x[1])
## Gradient of objective f(x)
def df(x):
return np.array((2*x[0] - 4 + x[1] - 1/x[0], 3*x[1] - 7 + x[0] - 1/x[1]))
## Gradient of inequality constraint g(x)
def dg(x):
return np.array((-x[1], -x[0]))
## Gradient of equality constraint h(x)
def dh(x):
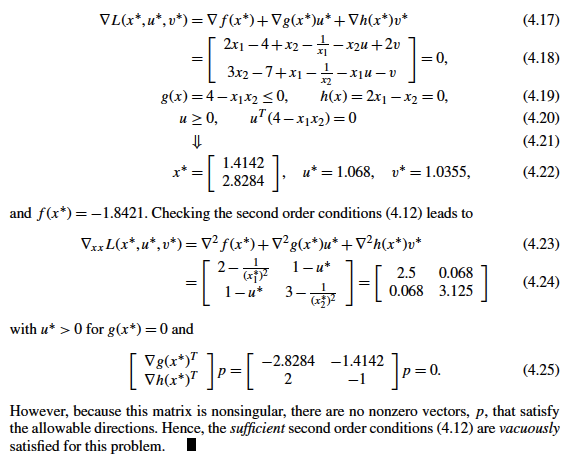
return np.array([2, -1])
## Function that plots contour of objective, solution, and optionally g(x) <= 0 and h(x) = 0
def visualize(xsln,plot_g,plot_h):
## Create contour plot
n1 = 101
n2 = 101
x1eval = np.linspace(0.05,10,n1)
x2eval = np.linspace(0.05,10,n2)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x1eval, x2eval)
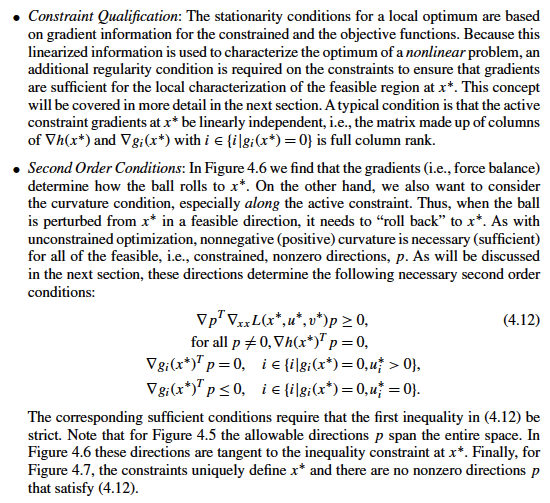
Z = np.zeros([n2,n1])
for i in range(0,n1):
for j in range(0,n2):
Z[j,i] = f((X[j,i], Y[j,i]))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
CS = ax.contour(X, Y, Z)
ax.clabel(CS, inline=1, fontsize=10)
## Plot g(x) <= 0
if(plot_g):
g_x2 = np.zeros(n1)
for i in range(0,n1):
# Inverted g(x) = 0 to calculate x2 explicitly from x1
g_x2[i] = 4 / x1eval[i]
plt.plot(x1eval,g_x2,color="blue",linestyle="-.",label="$g(x) \leq 0$")
## Plot h(x) = 0
if(plot_h):
h_x2 = 2*x1eval
plt.plot(x1eval,h_x2,color="red",linestyle="--",label="$h(x) = 0$")
## Plot solution
plt.scatter(xsln[0],xsln[1],marker="*",color="black",label="$x^{*}$")
## Adjust x and y limits
plt.xlim([-1,10])
plt.ylim([-1,10])
## Add legend
plt.legend()
## Function that draws gradient of f(x) and optionally g(x) and h(x)
def draw_gradients(x,with_g,with_h):
dh_x = dh(x)
## Draw gradient of f(x) [objective]
df_x = df(x)
plt.arrow(x[0],x[1],df_x[0],df_x[1],color="black",width=0.1)
## Draw gradient of g(x) [inequality]
if(with_g):
dg_x = dg(x)
plt.arrow(x[0],x[1],dg_x[0],dg_x[1],color="blue",width=0.1)
## Draw gradient of h(x) [equality]
if(with_h):
dh_x = dh(x)
plt.arrow(x[0],x[1],dh_x[0],dh_x[1],color="red",width=0.1)
def solve_opt(consider_g,consider_h):
## Create concrete Pyomo model
m = ConcreteModel()
## Declare variables with initial values
m.x1 = Var(bounds=(0,100),initialize=10)
m.x2 = Var(bounds=(0,100),initialize=10)
## Declare objective
m.OBJ = Objective(expr=m.x1**2 - 4*m.x1 + 1.5*m.x2**2 - 7*m.x2 + m.x1 * m.x2 + 9 - log(m.x1) - log(m.x2), sense = minimize)
if(consider_g):
## Add inequality constraint
m.con1 = Constraint(expr=4 - m.x1*m.x2 <= 0)
if(consider_h):
## Add equality constraint
m.con2 = Constraint(expr=2*m.x1 - m.x2 == 0)
## Specify IPOPT as solver
solver = SolverFactory('ipopt')
## Solve the model
results = solver.solve(m, tee = True)
## Return the solution
return [value(m.x1),value(m.x2)]
# Solve optimization problem
xsln = solve_opt(False,False)
# Create contour plot
visualize(xsln,False,False)
plt.show()
Ipopt 3.12.10:
******************************************************************************
This program contains Ipopt, a library for large-scale nonlinear optimization.
Ipopt is released as open source code under the Eclipse Public License (EPL).
For more information visit http://projects.coin-or.org/Ipopt
******************************************************************************
This is Ipopt version 3.12.10, running with linear solver mumps.
NOTE: Other linear solvers might be more efficient (see Ipopt documentation).
Number of nonzeros in equality constraint Jacobian...: 0
Number of nonzeros in inequality constraint Jacobian.: 0
Number of nonzeros in Lagrangian Hessian.............: 3
Total number of variables............................: 2
variables with only lower bounds: 0
variables with lower and upper bounds: 2
variables with only upper bounds: 0
Total number of equality constraints.................: 0
Total number of inequality constraints...............: 0
inequality constraints with only lower bounds: 0
inequality constraints with lower and upper bounds: 0
inequality constraints with only upper bounds: 0
iter objective inf_pr inf_du lg(mu) ||d|| lg(rg) alpha_du alpha_pr ls
0 2.4439483e+02 0.00e+00 3.29e+01 -1.0 0.00e+00 - 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 0
1 -8.0094510e-01 0.00e+00 4.03e-01 -1.0 8.53e+00 - 9.05e-01 1.00e+00f 1
2 -8.7120418e-01 0.00e+00 2.51e-03 -1.0 1.31e-01 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
3 -8.7421973e-01 0.00e+00 5.46e-04 -2.5 3.76e-02 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
4 -8.7422408e-01 0.00e+00 1.29e-06 -3.8 1.78e-03 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
5 -8.7422408e-01 0.00e+00 6.93e-10 -5.7 4.12e-05 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
6 -8.7422408e-01 0.00e+00 9.45e-14 -8.6 4.81e-07 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
Number of Iterations....: 6
(scaled) (unscaled)
Objective...............: -8.7422408318635370e-01 -8.7422408318635370e-01
Dual infeasibility......: 9.4500693109869893e-14 9.4500693109869893e-14
Constraint violation....: 0.0000000000000000e+00 0.0000000000000000e+00
Complementarity.........: 2.5065634500861016e-09 2.5065634500861016e-09
Overall NLP error.......: 2.5065634500861016e-09 2.5065634500861016e-09
Number of objective function evaluations = 7
Number of objective gradient evaluations = 7
Number of equality constraint evaluations = 0
Number of inequality constraint evaluations = 0
Number of equality constraint Jacobian evaluations = 0
Number of inequality constraint Jacobian evaluations = 0
Number of Lagrangian Hessian evaluations = 6
Total CPU secs in IPOPT (w/o function evaluations) = 0.010
Total CPU secs in NLP function evaluations = 0.000
EXIT: Optimal Solution Found.
# Solve optimization problem
xsln = solve_opt(True,False)
# Create contour plot
visualize(xsln,True,False)
# Draw gradient
draw_gradients(xsln,True,False)
plt.show()
Ipopt 3.12.10:
******************************************************************************
This program contains Ipopt, a library for large-scale nonlinear optimization.
Ipopt is released as open source code under the Eclipse Public License (EPL).
For more information visit http://projects.coin-or.org/Ipopt
******************************************************************************
This is Ipopt version 3.12.10, running with linear solver mumps.
NOTE: Other linear solvers might be more efficient (see Ipopt documentation).
Number of nonzeros in equality constraint Jacobian...: 0
Number of nonzeros in inequality constraint Jacobian.: 2
Number of nonzeros in Lagrangian Hessian.............: 3
Total number of variables............................: 2
variables with only lower bounds: 0
variables with lower and upper bounds: 2
variables with only upper bounds: 0
Total number of equality constraints.................: 0
Total number of inequality constraints...............: 1
inequality constraints with only lower bounds: 0
inequality constraints with lower and upper bounds: 0
inequality constraints with only upper bounds: 1
iter objective inf_pr inf_du lg(mu) ||d|| lg(rg) alpha_du alpha_pr ls
0 2.4439483e+02 0.00e+00 3.60e+00 -1.0 0.00e+00 - 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 0
1 4.4804168e+01 0.00e+00 3.92e+00 -1.0 2.13e+02 - 8.82e-01 4.46e-01f 1
2 5.4337665e+00 0.00e+00 1.68e+00 -1.0 2.39e+00 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
3 5.2037708e-02 0.00e+00 8.16e-01 -1.0 9.15e-01 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
4 -4.4584904e-01 0.00e+00 1.06e-01 -1.7 2.32e-01 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
5 -4.8930521e-01 0.00e+00 1.81e-03 -2.5 5.28e-02 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
6 -4.9427819e-01 0.00e+00 8.51e-06 -3.8 8.98e-03 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
7 -4.9445150e-01 0.00e+00 7.69e-09 -5.7 3.02e-04 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
8 -4.9445337e-01 0.00e+00 8.06e-13 -8.6 3.28e-06 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
Number of Iterations....: 8
(scaled) (unscaled)
Objective...............: -4.9445336916190996e-01 -4.9445336916190996e-01
Dual infeasibility......: 8.0590836175421712e-13 8.0590836175421712e-13
Constraint violation....: 0.0000000000000000e+00 0.0000000000000000e+00
Complementarity.........: 2.5083384199831901e-09 2.5083384199831901e-09
Overall NLP error.......: 2.5083384199831901e-09 2.5083384199831901e-09
Number of objective function evaluations = 9
Number of objective gradient evaluations = 9
Number of equality constraint evaluations = 0
Number of inequality constraint evaluations = 9
Number of equality constraint Jacobian evaluations = 0
Number of inequality constraint Jacobian evaluations = 9
Number of Lagrangian Hessian evaluations = 8
Total CPU secs in IPOPT (w/o function evaluations) = 0.012
Total CPU secs in NLP function evaluations = 0.000
EXIT: Optimal Solution Found.
# Solve optimization problem
xsln = solve_opt(True,True)
# Create contour plot
visualize(xsln,True,True)
# Draw gradient
draw_gradients(xsln,True,True)
plt.show()
Ipopt 3.12.10:
******************************************************************************
This program contains Ipopt, a library for large-scale nonlinear optimization.
Ipopt is released as open source code under the Eclipse Public License (EPL).
For more information visit http://projects.coin-or.org/Ipopt
******************************************************************************
This is Ipopt version 3.12.10, running with linear solver mumps.
NOTE: Other linear solvers might be more efficient (see Ipopt documentation).
Number of nonzeros in equality constraint Jacobian...: 2
Number of nonzeros in inequality constraint Jacobian.: 2
Number of nonzeros in Lagrangian Hessian.............: 3
Total number of variables............................: 2
variables with only lower bounds: 0
variables with lower and upper bounds: 2
variables with only upper bounds: 0
Total number of equality constraints.................: 1
Total number of inequality constraints...............: 1
inequality constraints with only lower bounds: 0
inequality constraints with lower and upper bounds: 0
inequality constraints with only upper bounds: 1
iter objective inf_pr inf_du lg(mu) ||d|| lg(rg) alpha_du alpha_pr ls
0 2.4439483e+02 1.00e+01 2.05e+00 -1.0 0.00e+00 - 0.00e+00 0.00e+00 0
1 4.4148045e+01 5.54e+00 2.30e+00 -1.0 2.13e+02 - 8.84e-01 4.46e-01f 1
2 8.2513369e+00 4.16e-01 1.12e+00 -1.0 3.36e+00 - 1.00e+00 9.25e-01f 1
3 1.0558961e+00 0.00e+00 8.05e-01 -1.0 9.84e-01 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
4 2.1482166e-01 0.00e+00 1.14e-01 -1.7 2.30e-01 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00f 1
5 1.6203098e-01 0.00e+00 9.32e-04 -2.5 2.25e-02 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
6 1.5801768e-01 0.00e+00 1.94e-06 -3.8 3.61e-03 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
7 1.5786332e-01 0.00e+00 1.79e-09 -5.7 1.44e-04 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
8 1.5786148e-01 0.00e+00 2.44e-13 -8.6 1.73e-06 - 1.00e+00 1.00e+00h 1
Number of Iterations....: 8
(scaled) (unscaled)
Objective...............: 1.5786147595031963e-01 1.5786147595031963e-01
Dual infeasibility......: 2.4449104235876087e-13 2.4449104235876087e-13
Constraint violation....: 0.0000000000000000e+00 0.0000000000000000e+00
Complementarity.........: 2.5065016939133549e-09 2.5065016939133549e-09
Overall NLP error.......: 2.5065016939133549e-09 2.5065016939133549e-09
Number of objective function evaluations = 9
Number of objective gradient evaluations = 9
Number of equality constraint evaluations = 9
Number of inequality constraint evaluations = 9
Number of equality constraint Jacobian evaluations = 9
Number of inequality constraint Jacobian evaluations = 9
Number of Lagrangian Hessian evaluations = 8
Total CPU secs in IPOPT (w/o function evaluations) = 0.011
Total CPU secs in NLP function evaluations = 0.000
EXIT: Optimal Solution Found.
Why are the gradient vectors not the same length? I thought the forces were balanced...